About Refractive Errors:
Glasses (or spectacles) and contact lenses are two of the most common ways of correcting refractive errors. In eyes with normal vision, light focuses on the light-sensitive retina at the back of the eye. Once the retina senses light, it converts the light into the image that you see.
In refractive errors, the eyes are unable to focus light on the retina. This results in blurred vision. The solution is glasses or contact lenses. These bend the beam of light so it focuses properly on the retina. This should restore clear vision.
Normal vision: In normal vision, light rays from an object focus on the retina.
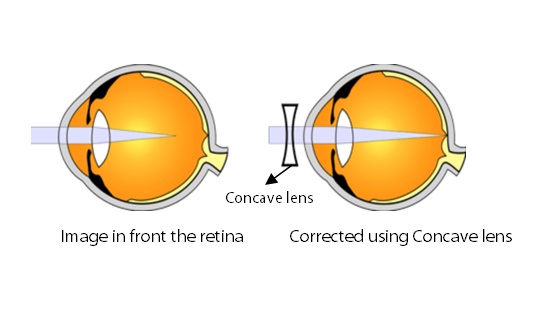
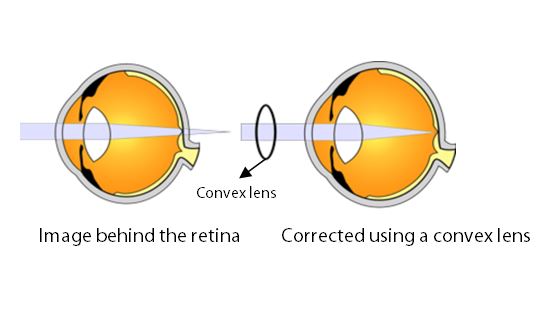
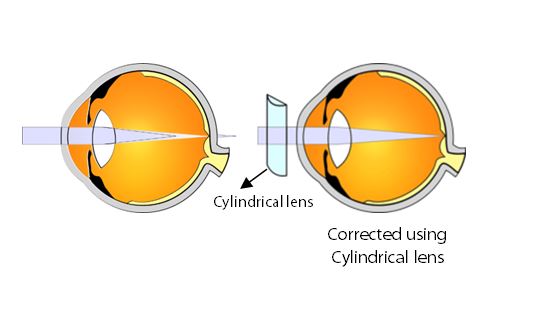
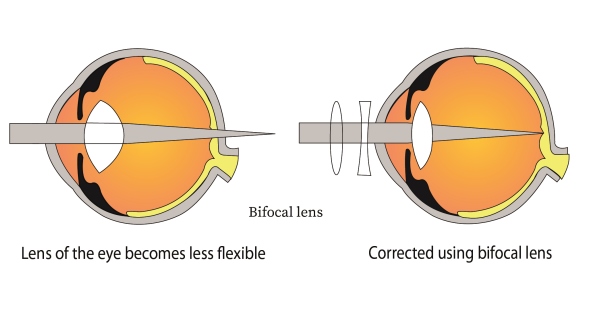
Refractive error: A refractive error is when the light rays focus either in front of or behind the retina. This causes blurred vision.
Types of Refractive Errors:
The four most common types are: